What is a Capacitor :-
• Capacitors
are
simple passive devices which are used to store
electricity. The capacitor has
the ability or “capacity” to store
energy in the form of an electrical charge
producing a potential
difference (Static Voltage)
across its plates, much like a small
rechargeable battery.
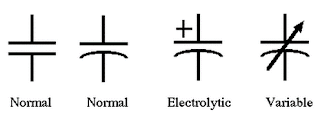
Capacitor Symbol :-
• A
capacitor is formed from two conducting plates separated by
air or by some
form of a good insulating material such as waxed
paper, mica, ceramic, plastic
or some form of a liquid gel. The
insulating layer between a capacitors plates
is commonly called
the Dielectric.
• Due
to this insulating layer, the d.c. current can not flow through
the
capacitor but instead a voltage is produced across the plates in
the form of an
electrical charge.
• If a current i flows, positive change, q, will accumulate on
the upper plate. To preserve charge neutrality, a balancing negative
charge will be present on the lower plate.
• Hence, there will be a potential energy difference (or
voltage v) between the plates which is proportional to the charge q.
• If a current i flows, positive change, q, will accumulate on
the upper plate. To preserve charge neutrality, a balancing negative
charge will be present on the lower plate.
• Hence, there will be a potential energy difference (or
voltage v) between the plates which is proportional to the charge q.
where, A is the area of the plates.
d is their separation.
Ɛ0
is the permittivity of the
insulating layer
( Ɛ0 = 8.85 pF/m for vacuum).
insulating layer
( Ɛ0 = 8.85 pF/m for vacuum).
• The capacitance is given by the following
expression :
The
capacitance is measured in Farads (F)
The
charge q is hence given by the expression :
• The
conductive metal plates of a capacitor can be either
square, circular or
rectangular, or they can be of a cylindrical or
spherical shape with the
general shape, size and construction of
a parallel plate capacitor depending on
its application and
voltage rating.
• When used in a direct current or DC circuit, a capacitor
charges up to its supply
voltage but blocks the flow of current
through it because the dielectric.
However, when a capacitor
is connected to an alternating current or AC circuit,
the flow
of the current appears to pass straight through the capacitor
with
little or no resistance.
Types of Capacitors :-
• There are a large variety of different types of
capacitor available in the market with
their own set of
characteristics and applications, from very small delicate
trimming capacitors up to large power metal-can type
capacitors used in high
voltage power correction and
smoothing circuits.
• Capacitor types are distinguished by the material used as
the insulator.
• Let us now discuss a few common types of capacitor
available.
Variable Capacitor Symbol :-
• Variable dielectric capacitors are multi-plate air-spaced
types that have a set of fixed
plates (the stator vanes) and
a set of movable plates (the rotor vanes) which
move in
between the fixed plates.
• The position of the moving plates with respect to the
fixed plates determines the
overall capacitance value.
• The capacitance is generally at maximum when the two
sets of plates are fully
meshed together.
• High voltage type tuning capacitors have relatively large
spacings or
air-gaps between the plates with breakdown
voltages reaching many thousands of
volts.
Variable Capacitor Symbol :-
Film Capacitor :-
• Film Capacitors
are the most commonly available of all
types of capacitors
• These capacitors have a relatively large family with the
difference being in their
dielectric properties which
include polyester (Mylar), polystyrene,
polypropylene,
polycarbonate , metalised paper, Teflon etc.
• Film type capacitors are available in capacitance ranges
from as small as
5pF to as large as 100uF .
• Film Capacitors which use polystyrene,
polycarbonate or
Teflon as their dielectrics are sometimes called “Plastic
capacitors”. The main advantage of plastic film capacitors
compared to
impregnated-paper types is that they operate
well under conditions of high
temperature, have smaller
tolerances, a very long service life and high
reliability.







Post a Comment
Welcome to BishwasEducation